Uploading Files
This guide explains how to upload files to Redbelt using our chunked upload API. This approach ensures reliable uploads for files of any size by breaking them into manageable parts.
There are four main steps:
- Start Upload Session
- Upload Parts
- Finish Upload
- Monitor Status
Prerequisites
Section titled “Prerequisites”Before uploading files, ensure you have:
- A valid API key (see API Quickstart)
- A folder ID where the file will be uploaded
- The file size must be ≤ 512 MB
Upload Flow Diagram
Section titled “Upload Flow Diagram”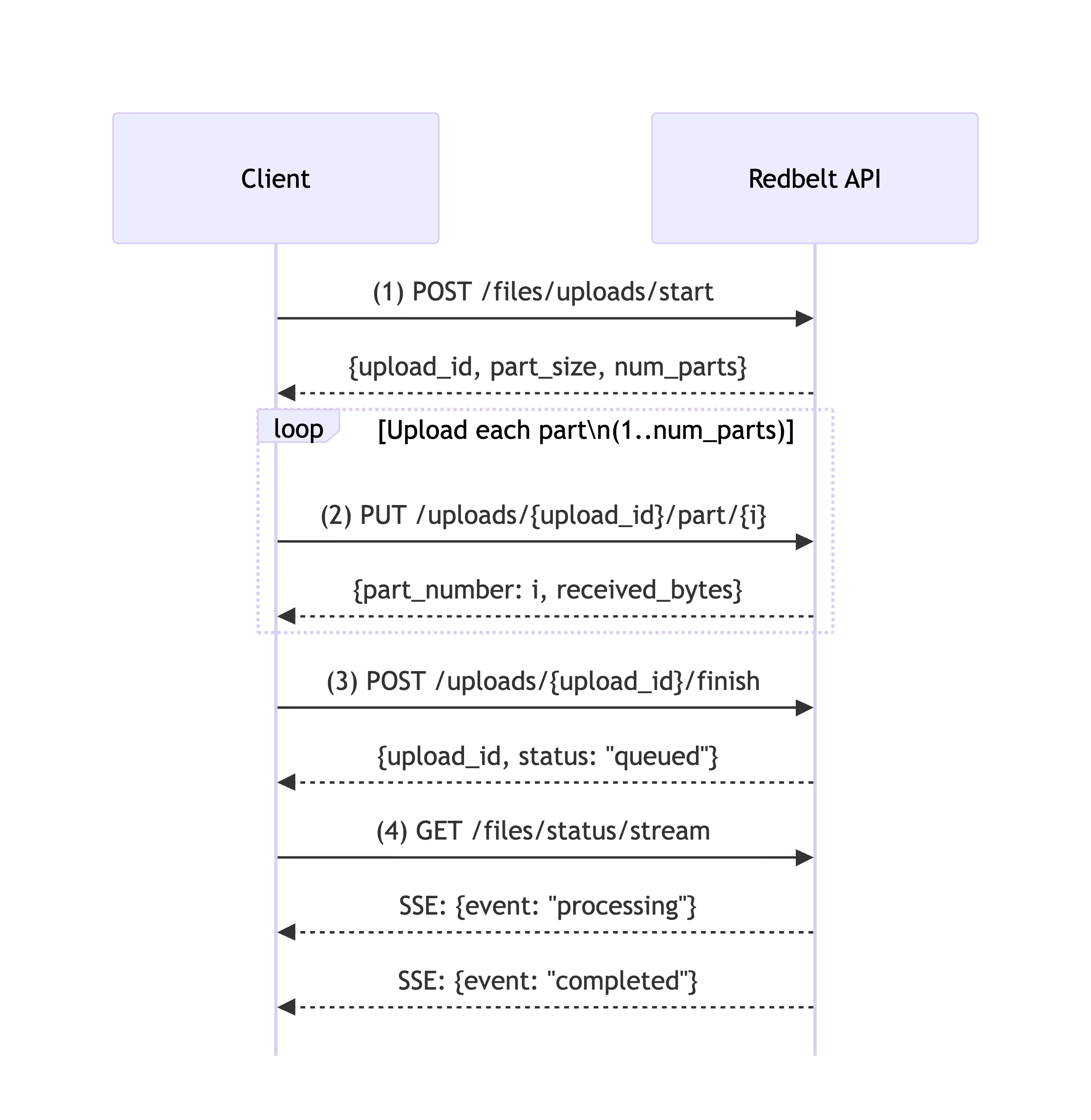
Step 1: Start Upload Session
Section titled “Step 1: Start Upload Session”Initialize an upload session to get the configuration for chunked uploads.
import osimport requestsfrom dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
api_url = "https://redbelt.ai/api"session = requests.Session()session.headers.update({ "Authorization": f"Bearer {os.getenv('REDBELT_API_KEY')}", "Content-Type": "application/json"})
file_path = "document.pdf"file_size = os.path.getsize(file_path)
start_payload = { "folder_id": "018c1234-5678-7abc-def0-123456789abc", "file_name": "document.pdf", "size": file_size, "metadata": {"source": "api"}, "tags": ["important"]}
response = session.post(f"{api_url}/files/uploads/start", json=start_payload)response.raise_for_status()
data = response.json()["data"]upload_id = data["upload_id"]part_size = data["part_size"]num_parts = data["num_parts"]
print(f"Upload session created: {upload_id}")print(f"Will upload {num_parts} parts of {part_size} bytes each")Step 2: Upload Parts
Section titled “Step 2: Upload Parts”Upload the file in chunks using the configuration from Step 1.
with open(file_path, "rb") as f: for part_number in range(1, num_parts + 1): if part_number < num_parts: chunk = f.read(part_size) else: chunk = f.read()
if chunk: part_url = f"{api_url}/files/uploads/{upload_id}/part/{part_number}" headers = { "Authorization": f"Bearer {os.getenv('REDBELT_API_KEY')}", "Content-Length": str(len(chunk)) }
response = requests.put(part_url, data=chunk, headers=headers) response.raise_for_status()
data = response.json()["data"] print(f"Uploaded part {data['part_number']}/{num_parts}: {data['received_bytes']} bytes")Step 3: Finish Upload
Section titled “Step 3: Finish Upload”Signal that all parts have been uploaded and trigger file processing.
finish_url = f"{api_url}/files/uploads/{upload_id}/finish"response = session.post(finish_url)response.raise_for_status()
finish_data = response.json()print(f"Upload completed. Status: {finish_data['data']['status']}")Step 4: Monitor Status
Section titled “Step 4: Monitor Status”Monitor the upload and processing status in real-time using Server-Sent Events (SSE).
Event Stream Format
Section titled “Event Stream Format”The endpoint returns Server-Sent Events in this format:
data: {"event": "part_uploaded", "upload_id": "...", "part_number": 1, "bytes": 5242880}
data: {"event": "queued", "upload_id": "...", "client_batch_id": "batch_001"}
data: {"event": "processing", "upload_id": "..."}
data: {"event": "completed", "upload_id": "..."}Event Types
Section titled “Event Types”| Event | Description |
|---|---|
part_uploaded | A file part was successfully uploaded |
queued | Upload finished and queued for processing |
processing | File is being processed |
completed | Processing completed successfully |
failed | Processing failed |
error | An error occurred |
Example
Section titled “Example”import jsonimport threading
def stream_status(upload_id): payload = {"upload_id": upload_id}
with session.get(f"{api_url}/files/status/stream", json=payload, stream=True) as resp: resp.raise_for_status()
for line in resp.iter_lines(decode_unicode=True): if not line or not line.startswith("data: "): continue
try: data = json.loads(line[len("data: "):]) event_type = data.get("event") print(f"Event: {event_type} - {data}")
if event_type in ("completed", "failed", "error"): break except json.JSONDecodeError as e: print(f"Failed to parse event: {e}")
status_thread = threading.Thread(target=stream_status, args=(upload_id,), daemon=True)status_thread.start()Common Errors
Section titled “Common Errors”400 Bad Request - File Too Large
Section titled “400 Bad Request - File Too Large”{ "message": "Max file size is 512 MB", "status_code": 400}401 Unauthorized
Section titled “401 Unauthorized”{ "message": "Unauthorized", "status_code": 401}404 Not Found - Invalid Upload Session
Section titled “404 Not Found - Invalid Upload Session”{ "message": "Upload session not found", "status_code": 404}Best Practices
Section titled “Best Practices”- Always validate file size before starting an upload (max 512 MB)
- Implement retry logic for failed part uploads
- Monitor status events to track processing progress
- Use client_batch_id when uploading multiple files to track them as a group
- Close status streams properly to avoid memory leaks
- Handle network interruptions gracefully by checking upload session state
Supported File Types
Section titled “Supported File Types”Redbelt automatically detects and processes various file types:
- Documents: PDF, DOC, DOCX, TXT, RTF, HTML
- Spreadsheets: XLS, XLSX, CSV
- Presentations: PPT, PPTX
- Images: PNG, JPG, JPEG, GIF, SVG, WEBP
- Audio: MP3, MPEG, MPGA, M4A, WAV, WEBM
- Video: MP4
- Email: MSG, OFT, EML
- Data: JSON
- Code: MD, SQL, PY, JAVA, JS
Need Help?
Section titled “Need Help?”- 📖 Check out our API Quickstart Guide
- 📖 Our Full API Reference has more details on the API
- 📧 Contact support@redbelt.ai